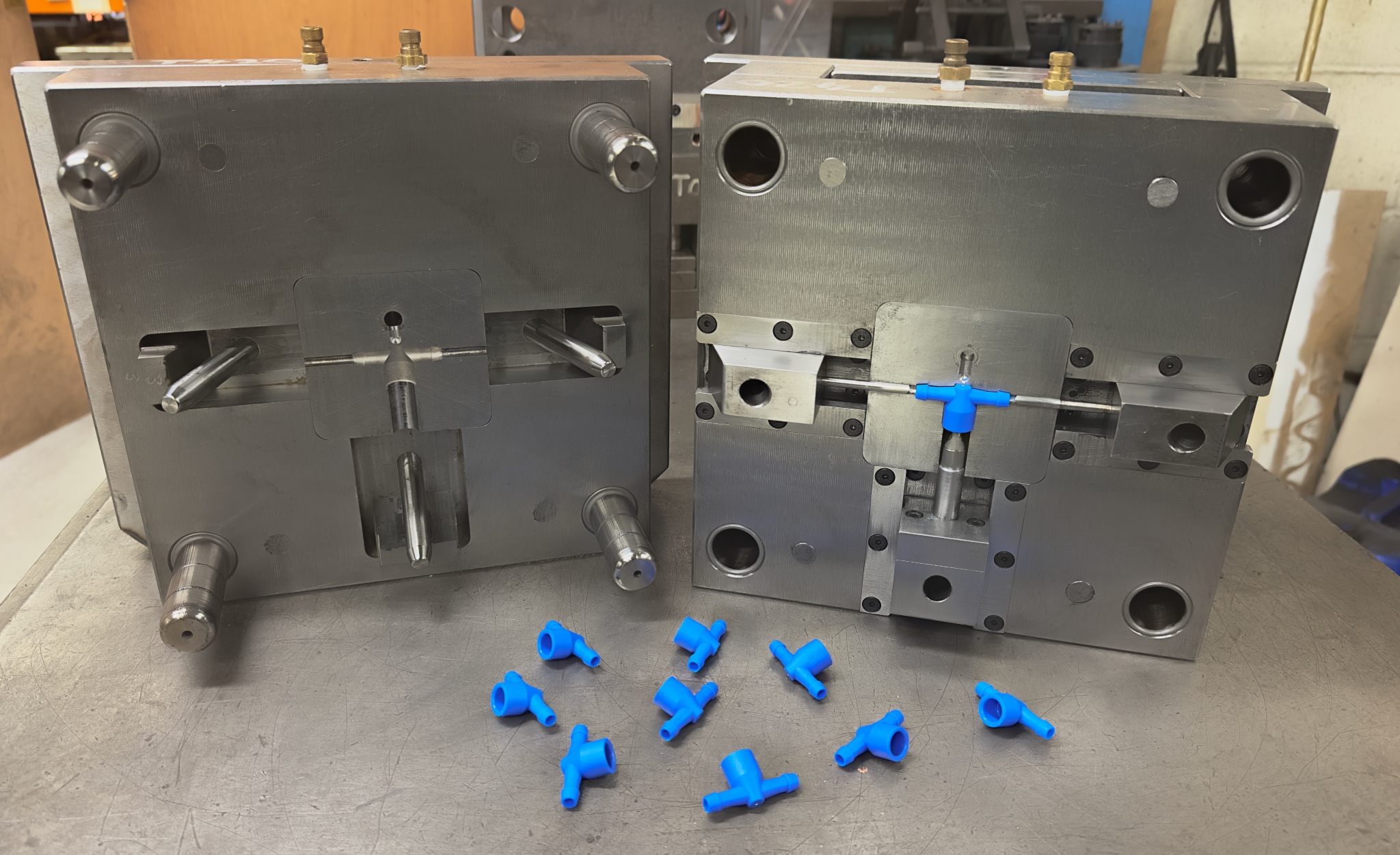
Injection moulding process
Injection Moulding Process: A Complete Guide for
Manufacturers
Injection moulding is one of the most important and widely used
manufacturing processes for producing high-precision plastic parts at scale.
Whether you're in the automotive, medical, electronics, or consumer goods
industry, the injection moulding process offers unmatched efficiency,
repeatability, and design flexibility.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through what injection moulding
is, how it works, its technical specifications, advantages, and key
considerations. We’ll also answer the most frequently asked questions to help
you better understand its applications.
What is Injection Moulding?
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process used to produce
parts by injecting molten material into a mould. Most commonly used with thermoplastic
and thermosetting polymers, the process is ideal for creating high-volume
parts with tight tolerances and complex geometries.
The process is highly automated, making it a cost-effective choice for
mass production.
How the Injection Moulding Process
Works
Injection moulding involves a series of systematic steps to ensure
precise shaping of plastic materials into finished products.
1. Mould Clamping
The process begins with clamping the mould halves together using a
powerful hydraulic or mechanical press. This forms a closed cavity for the
molten plastic.
2. Material Injection
Plastic pellets are fed into a heated barrel, melted, and injected into
the mould at high pressure through a screw system.
3. Cooling Phase
Once inside the mould, the plastic cools and solidifies into the final
shape. The cooling time depends on part thickness and material type.
4. Ejection
After the plastic has solidified, the mould opens, and ejector pins push
the finished part out of the cavity.
Injection Moulding Specifications
Below are the common specifications and parameters that define the
performance and capabilities of an injection moulding system:
|
Parameter |
Specification |
|
Materials |
Thermoplastics, Thermosets, Elastomers |
|
Injection Pressure |
70 to 140 MPa |
|
Clamping Force |
20 to 5,000 tons |
|
Shot Size |
1 gram to several kilograms |
|
Mould Cavity Pressure |
35 to 140 MPa |
|
Cycle Time |
10 to 60 seconds |
|
Tolerances |
±0.1 mm or tighter |
|
Surface Finishes |
Smooth, Textured, Matte, Glossy |
|
Tooling Materials |
Steel, Aluminum |
Advantages of Injection Moulding
Injection moulding offers a variety of benefits that make it the go-to
process for manufacturing plastic parts:
1. High Production Efficiency
The cycle times are short, and once the tooling is developed, parts can
be produced rapidly in high volumes.
2. Precision and Consistency
Ideal for producing parts with complex geometries and tight tolerances
across millions of cycles.
3. Material Variety
Compatible with a wide range of materials to achieve desired physical,
chemical, and aesthetic properties.
4. Minimal Waste
The process generates little material waste, and excess material can
often be reground and reused.
5. Low Labor Costs
Highly automated machines reduce manual labor and increase cost
efficiency.
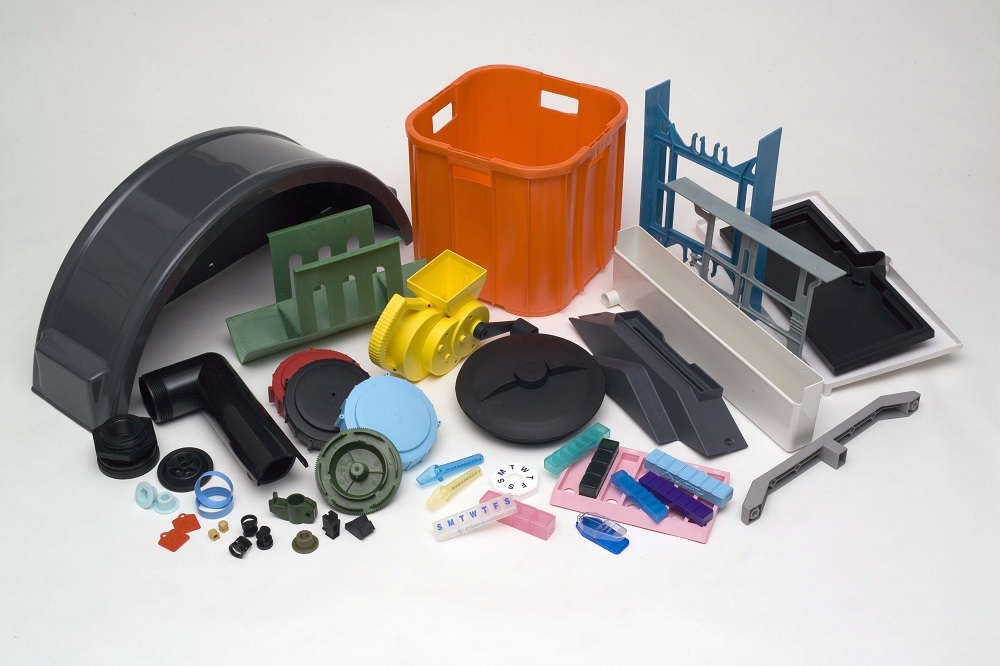
Applications of Injection Moulding
Injection moulding is used across a wide spectrum of industries due to
its flexibility and reliability:
- Automotive: Dashboards,
bumpers, gear knobs
- Consumer
Products: Plastic containers, toys, appliance components
- Medical: Syringes,
diagnostic devices, prosthetics
- Packaging: Bottle caps,
closures, custom packaging
- Electronics: Phone
housings, connectors, circuit board casings
Key Design Considerations
Before starting the injection moulding process, consider the following
design principles for optimal performance:
1. Wall Thickness
Maintain uniform wall thickness to prevent defects like warping or sink
marks.
2. Draft Angles
Add tapering to vertical walls to facilitate smooth ejection from the
mould.
3. Undercuts and Ribs
Minimize undercuts to reduce tooling complexity and incorporate ribs for
structural strength.
4. Material Selection
Choose materials based on impact strength, flexibility, heat resistance,
or regulatory requirements.
FAQs About the Injection Moulding
Process
Q1. What materials are best suited for
injection moulding?
A: Common materials include ABS, Polypropylene, Nylon, Polyethylene, and
Polystyrene. The best material depends on your part’s function and environment.
Q2. What is the cost of creating an
injection mould?
A: Tooling costs can range from $5,000 to over $100,000 depending on size,
complexity, and material of the mould. However, the cost per part decreases
with volume.
Q3. Can injection moulding be used for
low-volume production?
A: While it’s traditionally used for high volumes, low-volume runs are
possible with aluminum moulds or rapid tooling methods.
Q4. How long does a mould last?
A: A steel mould can last for over a million cycles with proper
maintenance, while aluminum tools have shorter lifespans.
Q5. Is injection moulding
environmentally friendly?
A: It can be sustainable when using recyclable plastics and optimizing
material usage. Energy-efficient machines and regrind systems also reduce the
environmental footprint.
Final Thoughts
Injection moulding is a time-tested manufacturing technique that provides
speed, precision, and scalability. With careful attention to design, tooling,
and material selection, it can help companies across industries bring
high-quality products to market efficiently.
Whether
you’re prototyping a new product or scaling up for mass production,
understanding the injection moulding process is essential for achieving both
quality and cost-effectiveness.