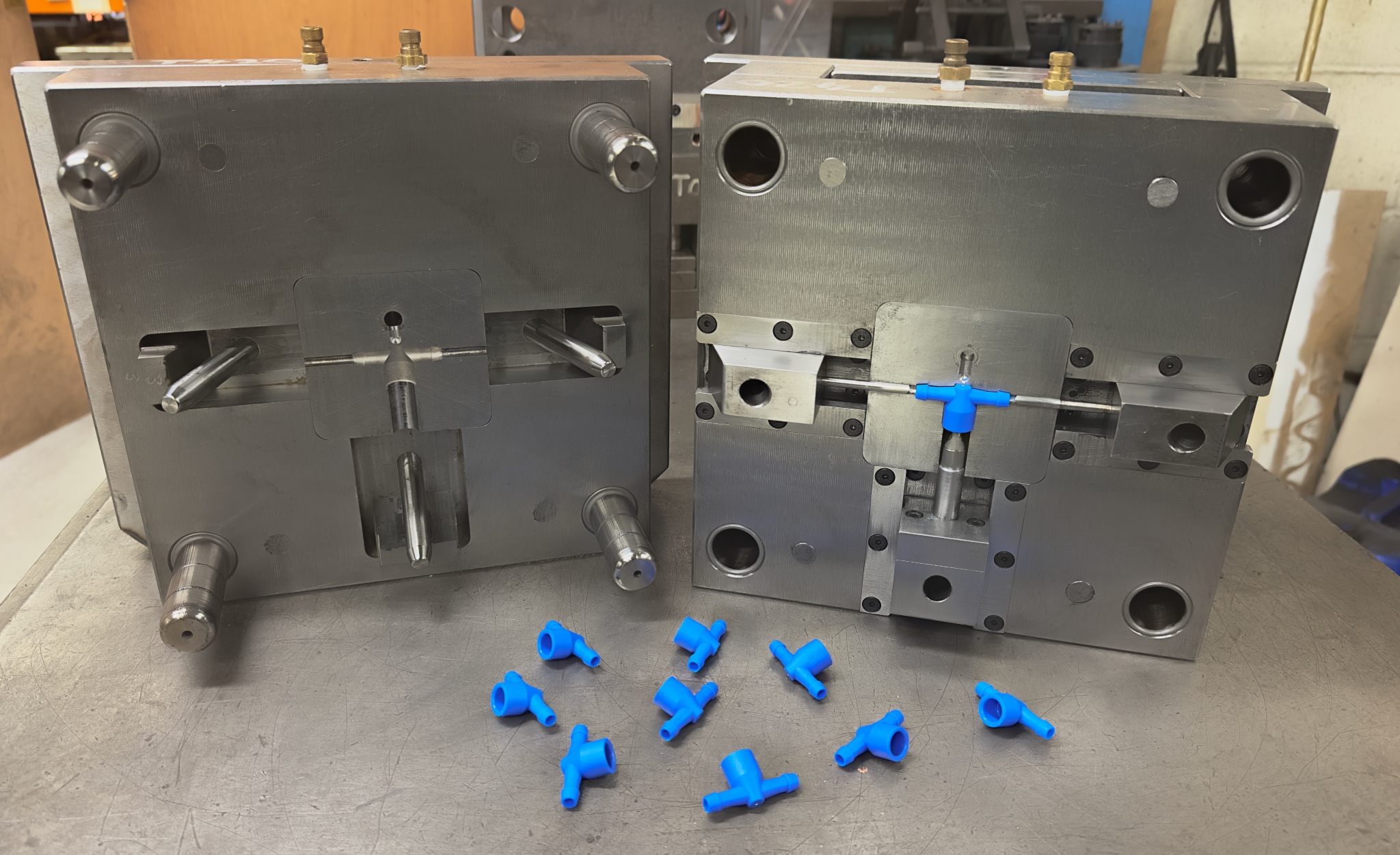
Mould development process
Understanding the Mould Development
Process: A Comprehensive Guide
Mould development plays a pivotal role in various industries,
particularly in manufacturing, where precision and efficiency are paramount.
Whether you're creating plastic components, automotive parts, or any other
product requiring moulds, understanding the development process is essential
for ensuring high-quality results. This guide will walk you through the stages
of mould development, key specifications to consider, and common challenges
manufacturers face.
What is Mould Development?
Mould development is the process of designing and creating a mould, a
tool used to shape materials into a specific form. These moulds can be made
from a variety of materials, including steel, aluminum, or other metals, and
are used in injection molding, compression molding, and other manufacturing
techniques. Moulds are crucial in ensuring that products are made with the
correct dimensions, strength, and durability.
Stages of the Mould Development
Process
The process of mould development is intricate and involves several
phases, from initial design to the final production run. Let's break down each
step:
1. Conceptualization and Design
The first stage in mould development involves designing the mould based
on the product’s specifications. This step requires collaboration between
engineers, designers, and manufacturers. Computer-aided design (CAD) software
is typically used to create a digital representation of the product and the
mould. This design will dictate the shape, size, and features of the final
mould. Specifications to consider include:
- Material choice: The type of
material selected for the mould will impact its durability and
performance. Common materials include hardened steel, aluminum, and
various alloys.
- Shape and size
of the product: The mould design needs to accommodate the product’s dimensions,
complexity, and any specific design features like holes, threads, or
undercuts.
- Cooling
channels: To prevent defects like warping, efficient cooling channels need
to be incorporated into the mould design to maintain a consistent
temperature during the molding process.
2. Mould Fabrication
Once the design is finalized, the next step is to fabricate the mould.
This phase involves precision machining, which can include:
- CNC machining: Computer
Numerical Control (CNC) machines are used to cut, shape, and carve the
mould based on the CAD design. CNC machines provide high precision,
ensuring that the final mould is accurate.
- Injection and
molding tools: These tools are carefully crafted to create cavities, channels,
and other essential features required for molding the desired product. The
design must ensure that the part can be easily ejected from the mould once
it’s formed.
3. Mould Testing and Trial Runs
After fabrication, the mould undergoes testing and trial runs. During
this phase, manufacturers inject the raw material into the mould to ensure that
it can create the product without issues. The goal of the trial run is to
detect any design flaws or issues, such as:
- Incomplete
filling of the cavity.
- Surface defects
such as air bubbles or excessive flash.
- Difficulty
ejecting the product.
If the product does not meet specifications, adjustments are made to the
mould design, cooling system, or injection process. Multiple trial runs may be
necessary to perfect the mould.
4. Final Production and Optimization
Once the trial run is successful and the mould is deemed optimal,
full-scale production begins. In this stage, the mould is used to manufacture
large quantities of the product. During this phase, the process is constantly
monitored and optimized to ensure maximum efficiency and product quality. Key
factors include:
- Cycle time: The time it
takes to produce each part. Shorter cycle times lead to higher production
rates.
- Material waste: Efforts are
made to minimize waste and optimize the use of raw materials during the
manufacturing process.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance
of the mould is crucial to ensure its longevity and consistent performance
throughout production.
5. Post-Production and Quality Control
After the production run, products undergo quality control to ensure they
meet the required standards. The mould is also inspected for wear and tear, and
any necessary repairs or modifications are made. If the mould is used for a
high-volume production run, it may need periodic refurbishment to maintain
optimal performance.
Key Specifications to Consider in
Mould Development
When developing a mould, several key specifications must be taken into
account to ensure its success in production:
- Material
selection: The type of material used for both the mould and the product plays
a significant role in the mould's longevity and the product’s strength.
For example, hardened steel is often used for molds that require long
lifespans and high precision.
- Mould cavity: The cavity is
where the molten material is injected. The design of the cavity must
account for uniform flow, cooling, and easy removal of the part.
- Mould lifespan: The lifespan
of the mould depends on factors such as material hardness, cooling system
efficiency, and maintenance practices.
- Tolerances and
finishes: The mould must be designed with very tight tolerances to ensure
the product meets the necessary specifications. Surface finishes are also
important for aesthetics and functionality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What materials are commonly used in
mould development?
Moulds can be made from various materials, including hardened steel,
aluminum, and beryllium copper alloys. Each material has its own advantages
depending on the application, such as hardness, resistance to wear, and heat
dissipation.
2. How long does the mould development
process take?
The time required for mould development can vary depending on the
complexity of the product and the mould itself. On average, the process can
take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, particularly when multiple
iterations of testing and adjustments are required.
3. What is the cost of developing a
mould?
The cost of mould development depends on factors such as the size and
complexity of the mould, material used, and the number of trial runs required.
Simple moulds can cost a few thousand dollars, while more intricate and
large-scale moulds can exceed tens of thousands.
4. How do I know if my mould needs
maintenance?
Moulds require regular inspections for signs of wear and tear, such as
cracks, rust, or degradation of the cooling system. If defects begin to appear
in the molded parts, it may be time for maintenance or refurbishment.
5. What are some common challenges in
mould development?
Challenges in mould development include issues with design accuracy,
material selection, cooling inefficiencies, and difficulties in product
ejection. Each of these challenges can impact production efficiency and product
quality.
Conclusion
The mould development process is a critical aspect of modern manufacturing. From the initial design to the final product, each step of the process plays a crucial role in determining the quality and efficiency of the manufacturing process. By understanding the stages involved and the specifications required, manufacturers can ensure that their moulds deliver precise, high-quality products while minimizing costs and production time