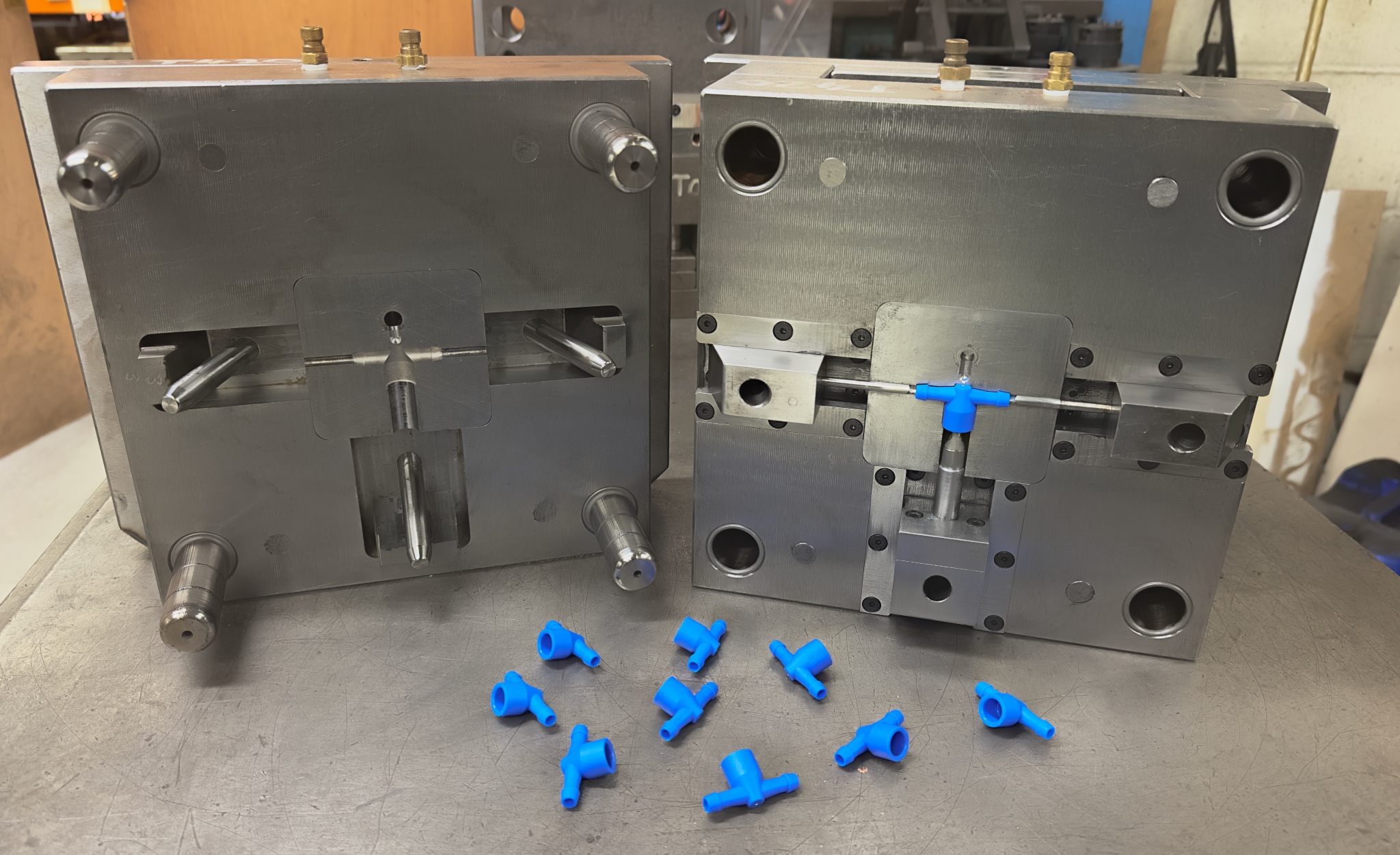
Plastic Injection Molded Parts
Plastic Injection Molded Parts: The
Backbone of Modern Manufacturing
Plastic injection molding is one of the most common and versatile manufacturing
processes in the world today. It’s used to create a vast array of products,
from everyday household items to high-precision automotive and medical
components. The plastic injection molded parts that result from this
process are critical in many industries due to their precision, durability, and
cost-effectiveness.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the world of plastic injection molded
parts, dive into the process, specifications, and applications, and answer some
common questions to help you better understand how these parts are made and
their importance in various industries.
What Are Plastic Injection Molded
Parts?
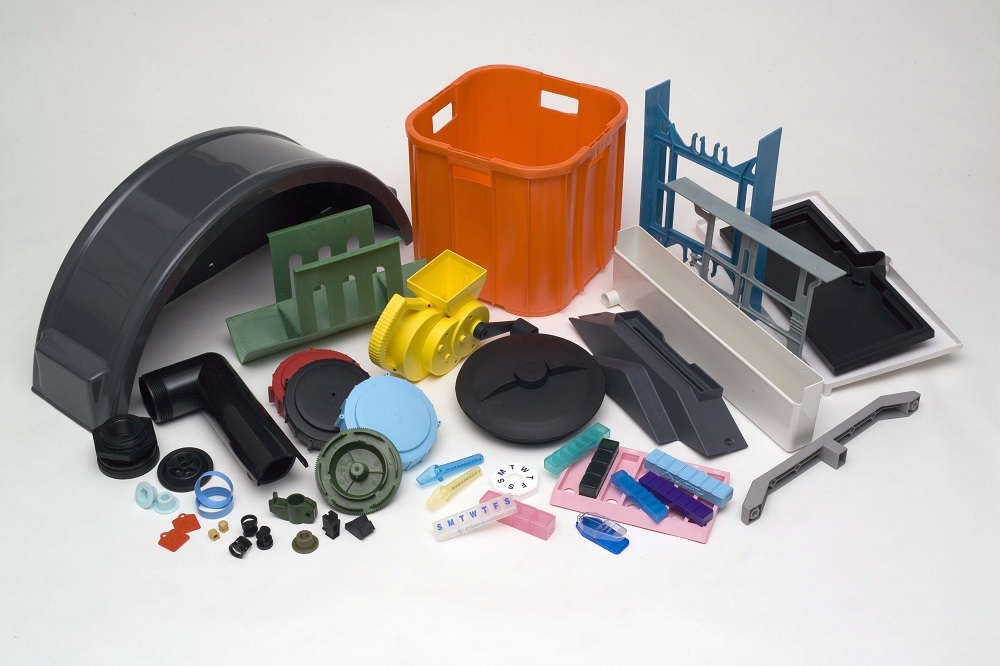
Plastic injection molded parts are components created using the injection
molding process. This process involves injecting molten plastic into a mold
cavity at high pressure. Once cooled, the plastic solidifies, taking the shape
of the cavity, resulting in a finished part. This method is highly efficient
and ideal for producing large volumes of identical parts with high precision.
These molded parts are used in a wide variety of applications, from
consumer electronics to automotive parts, medical devices, and packaging
materials. The versatility and adaptability of plastic injection molding make
it the preferred choice for manufacturers across the globe.
The Plastic Injection Molding Process
1. Material Selection
The first step in producing plastic injection molded parts is choosing
the right material. Depending on the part’s intended use, manufacturers select
from a range of plastic materials such as ABS, Polycarbonate, Nylon,
Polypropylene, and PVC. Each material has unique properties that
make it suitable for different applications.
2. Mold Design and Fabrication
The next step involves designing the mold, which is a critical part of
the process. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software is used to create a 3D
model of the part. Once the design is finalized, the mold is fabricated,
usually from high-quality steel or aluminum, depending on the
production requirements. The mold must be precisely manufactured to ensure that
the resulting parts are accurate and consistent.
3. Injection and Cooling
Once the mold is ready, the plastic material, typically in pellet form,
is heated until it becomes molten. The molten plastic is injected into the mold
under high pressure, where it fills the cavity. Afterward, the part is allowed
to cool and solidify within the mold. This cooling time varies depending on the
material used and the thickness of the part.
4. Ejection and Finishing
After the part has cooled and solidified, it is ejected from the mold. At
this stage, some parts may require additional finishing, such as trimming,
polishing, or painting to meet aesthetic or functional
requirements. The finished parts are then inspected for quality and consistency
before being packaged for shipment.
Specifications of Plastic Injection
Molded Parts
The success of plastic injection molded parts is determined by several
key specifications. Understanding these factors is essential for ensuring that
the final parts meet both functional and quality standards. Here are some
critical specifications to consider:
|
Specification |
Details |
|
Material Options |
ABS, Polycarbonate, Nylon, Polypropylene, PVC, and more |
|
Tolerance |
Tolerances can range from ±0.01 mm to ±0.05 mm |
|
Part Size |
Small components (e.g., connectors) to large parts (e.g., bumpers) |
|
Injection Pressure |
Ranges from 10,000 to 30,000 PSI depending on material and part
size |
|
Cycle Time |
Typically 15 to 60 seconds per cycle |
|
Surface Finish |
SPI grades, mirror finish, textured finishes, matte, glossy |
|
Part Complexity |
Simple to highly intricate geometries, including multi-cavity molds |
|
Production Volume |
Ideal for medium to high-volume production |
These specifications allow manufacturers to create parts that meet
precise functional and aesthetic requirements.
Applications of Plastic Injection
Molded Parts
Plastic injection molded parts are found in almost every industry. Below
are some examples of how they are applied:
1. Automotive Industry
Plastic injection molded parts are widely used in the automotive sector.
Components like dashboard parts, bumpers, interior panels,
and headlight housings are commonly made using injection molding. The
ability to produce parts with precise tolerances ensures they fit perfectly and
perform optimally.
2. Medical Devices
In the medical industry, plastic injection molded parts are
essential for creating syringes, IV connectors, surgical
instruments, and diagnostic devices. These parts must meet strict
regulatory standards for safety, sterility, and functionality. The precision of
injection molding ensures these parts are reliable in critical healthcare
applications.
3. Electronics
Plastic components are often used in mobile phones, laptops,
television sets, and computer peripherals. Injection molded parts
such as housings and connectors are designed to protect
electronic circuits and enable easy assembly of electronic devices.
4. Consumer Goods and Packaging
Plastic injection molding is a cost-effective way to produce high-quality
parts for a wide range of consumer goods, including kitchen utensils, toys,
and packaging materials. The versatility of this process allows for the
production of both small and large items with a high degree of customization.
FAQs About Plastic Injection Molded
Parts
Q1: What materials are commonly used
for plastic injection molded parts?
A: Common materials include ABS, Polycarbonate, Polypropylene,
Nylon, PVC, and Polyethylene. The choice of material
depends on the intended use of the part, including factors like strength,
flexibility, temperature resistance, and cost.
Q2: How long does the plastic
injection molding process take?
A: The time to produce plastic injection molded parts can vary. For prototype
parts, it may take several weeks, while for mass production, parts
can be produced in seconds to minutes per cycle. Production volume and
part complexity affect the timeline.
Q3: Can plastic injection molding be
used for both small and large parts?
A: Yes, plastic injection molding can be used to produce parts ranging from
small components like connectors to large parts like automotive bumpers. The
mold size and equipment used will vary based on part size.
Q4: What are the advantages of using
plastic injection molding?
A: The main advantages of plastic injection molding include high
precision, fast cycle times, low waste, and cost-effectiveness
for high-volume production. It also allows for the use of multiple materials
and the ability to create complex geometries.
Q5: Can plastic injection molded parts
be customized?
A: Yes, plastic injection molded parts can be highly customized in terms of
size, shape, color, and surface finish. Custom
molds can be designed to meet the specific needs of a product or application.
Conclusion
Plastic injection molded parts play a vital role in modern
manufacturing across various industries. The precision, versatility, and
efficiency of the injection molding process make it the go-to solution
for producing high-quality plastic components in large volumes. Whether for
automotive, medical, electronics, or consumer goods, these parts are
indispensable in creating products that are reliable, functional, and
cost-effective.
If you are looking to have plastic parts manufactured using injection molding, understanding the process, material options, and specifications is essential to ensure the quality and performance of your products.