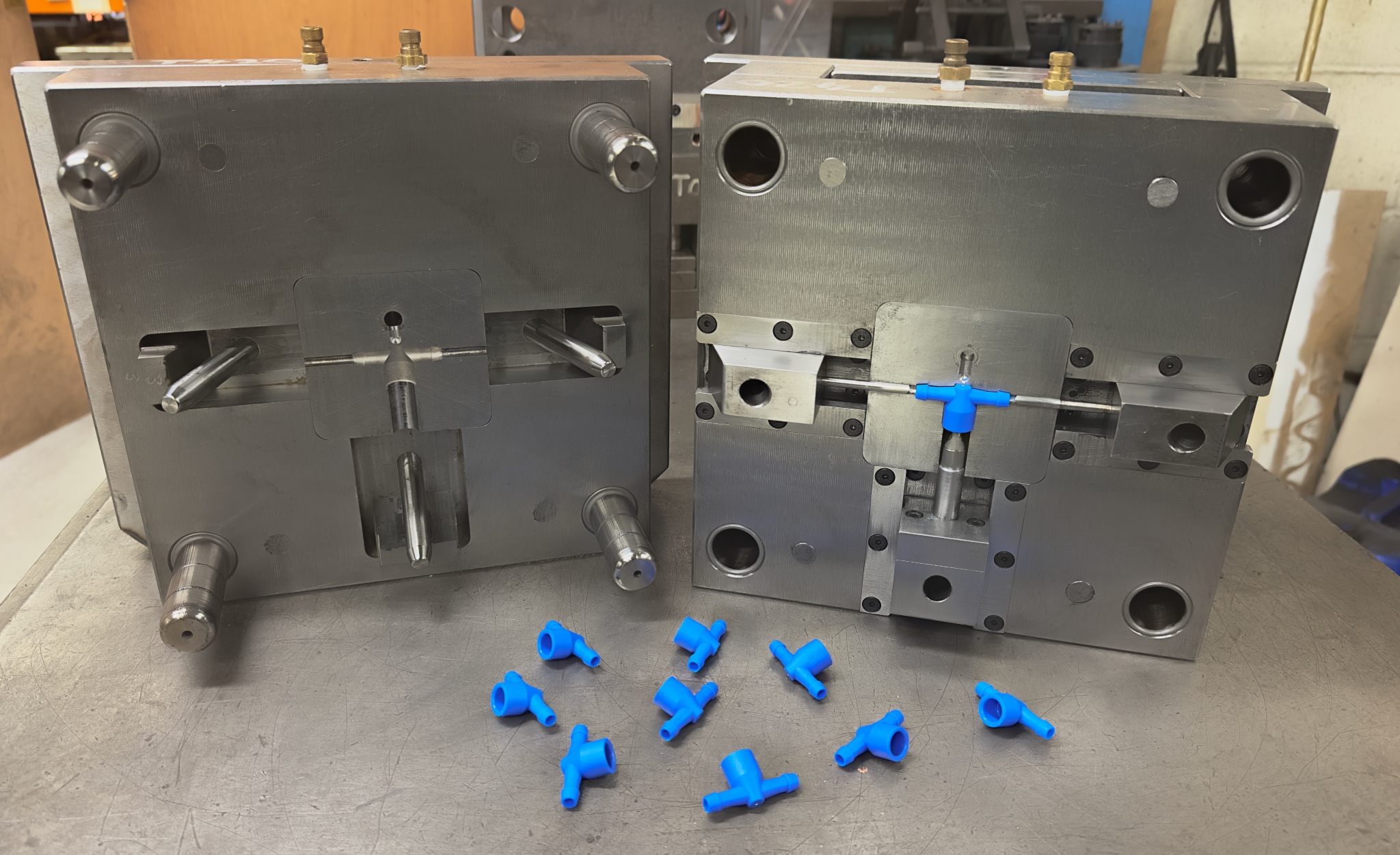
Plastic injection mould design
A Comprehensive Guide to Plastic
Injection Mould Design
Plastic injection moulding is one of the most widely used manufacturing
processes for producing plastic parts with high precision and efficiency. The
process involves injecting molten plastic into a mould, where it cools and
solidifies to form the desired shape. While the injection moulding process is
relatively simple, the design of the plastic injection mould itself plays a
critical role in the overall quality, cost, and speed of production. In this
blog post, we will explore the key elements of plastic injection mould design,
including specifications and best practices for achieving optimal results.
What is Plastic Injection Mould
Design?
Plastic injection mould design refers to the process of designing a mould
that will be used in the plastic injection moulding process to produce plastic
parts. The mould is essentially a hollowed-out shape into which molten plastic
is injected under high pressure. Once the plastic cools and solidifies, the
part can be ejected from the mould.
The design of the mould is critical to the success of the injection moulding
process, as it directly impacts the quality of the final product. A
well-designed mould ensures consistent production of high-quality parts,
reduces cycle times, minimizes material waste, and ensures the longevity of the
mould.
Key Stages of Plastic Injection Mould
Design
The design of a plastic injection mould involves several stages, each
requiring careful consideration of various factors, such as part geometry,
material properties, and mould material selection. Below are the main stages
involved in the design process:
1. Part Design and Material Selection
Before designing the mould, it is essential to have a clear understanding
of the part that will be produced. The part's geometry, dimensions, and
functionality will influence the mould design. Key factors to consider during
part design include:
- Wall thickness: Consistent
wall thickness ensures uniform flow of the molten plastic, reducing the
risk of defects like warping or sink marks.
- Undercuts: These are
areas of the part that are difficult to mould due to their shape. Special
mould features, such as lifters or slides, may be needed to release parts
with undercuts.
- Radii and
fillets: Sharp corners and edges should be avoided in part design, as they
can lead to stress concentrations and affect the part's strength.
Material selection is also critical. The type of plastic used influences
the design and performance of the mould. Common plastic materials include ABS,
polycarbonate, and polypropylene, each with its own properties and processing
requirements.
2. Mould Design and CAD Modeling
Once the part design and material are selected, the next step is the
actual mould design. This phase typically involves the use of Computer-Aided
Design (CAD) software to create a 3D model of the mould. The design must account
for various factors, including:
- Gate design: The gate is
the point through which the molten plastic enters the mould cavity. The
gate’s location, size, and type (e.g., edge, submarine, or pin gate)
influence the flow of material and the appearance of the part.
- Cooling system: An efficient
cooling system is essential for reducing cycle times and ensuring uniform
part quality. The design should include strategically placed cooling
channels that maintain a consistent temperature throughout the mould.
- Ejection system: The ejection
system is responsible for removing the part from the mould once it has
cooled. The design must include ejector pins or plates that apply uniform
force to ensure smooth ejection without damaging the part.
3. Mould Fabrication and Testing
After the mould design is finalized, it is time to fabricate the mould.
This involves precision machining of the mould cavities, cooling channels, and
other features based on the CAD model. Common fabrication methods include CNC
machining, electrical discharge machining (EDM), and wire EDM.
Once the mould is fabricated, it undergoes a series of test injections to
verify that it functions as intended. During these tests, the design may be
adjusted to address issues like incomplete filling, warping, or surface
defects. Multiple iterations of testing and refinement may be required to
ensure that the mould produces high-quality parts consistently.
4. Production and Optimization
Once the mould is tested and validated, it can be used for full-scale production.
During this phase, production parameters such as injection pressure,
temperature, and cycle time are optimized to ensure high-quality parts are
produced efficiently. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the mould are
necessary to prevent wear and tear, ensuring that the mould remains in good
condition throughout its lifespan.
Specifications to Consider in Plastic
Injection Mould Design
When designing a plastic injection mould, there are several important
specifications to consider to ensure that the mould performs efficiently and
produces high-quality parts:
1. Material Selection
The type of plastic used for the part determines many aspects of the
mould design, including the injection pressure, cooling rate, and material
flow. Factors such as the material’s melt temperature, shrinkage rate, and
viscosity must be considered to optimize the mould design.
2. Mould Durability
The mould must be designed for durability to withstand the stresses of
repeated injection cycles. Materials like hardened steel or beryllium-copper
alloys are commonly used for high-durability moulds, as they can resist wear
and maintain precision over time.
3. Part Design Features
The part design plays a major role in mould design. Features such as
thickness variations, ribs, bosses, holes, and threads need to be considered to
ensure that the part can be easily molded without defects. Proper venting and
gating are also necessary to avoid air traps and ensure smooth material flow.
4. Tolerances
Mould design must account for tight tolerances to ensure that parts meet
the required specifications. This includes considerations such as dimensional
accuracy, surface finish, and assembly fit.
FAQs About Plastic Injection Mould
Design
1. What is the importance of gate
design in injection moulding?
The gate design is critical because it controls the flow of molten
plastic into the mould cavity. A poorly designed gate can lead to defects such
as uneven filling, sink marks, or warping. Proper gate placement and size are
essential for high-quality parts.
2. How long does it take to design a
plastic injection mould?
The design process can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months,
depending on the complexity of the part and the mould. Detailed analysis and
testing are required to ensure that the mould performs efficiently and produces
parts with the desired quality.
3. Can injection moulds be used for
high-volume production?
Yes, plastic injection moulds are designed for high-volume production.
Once the mould is created, it can be used to produce thousands or even millions
of parts, making it ideal for mass production of plastic components.
4. What are the common challenges in
plastic injection mould design?
Some common challenges include managing complex part geometries, ensuring
proper cooling, preventing material defects, and optimizing cycle times. Mould
wear and tear can also impact the performance and longevity of the mould.
5. How can I improve the efficiency of
the injection moulding process?
Improving efficiency can be achieved through optimized mould design, such
as ensuring proper gate placement, enhancing cooling system design, and
reducing cycle time. Additionally, regular maintenance and careful material
selection can enhance process efficiency.
Conclusion
Plastic injection mould design is a complex and crucial process that requires careful attention to detail, from the part design to the final production run. A well-designed mould ensures high-quality plastic parts, efficient production, and reduced costs. By understanding the key specifications and stages of the design process, manufacturers can optimize their mould designs for maximum performance and reliability. Whether you're producing small components or large quantities, investing in the right mould design is essential for achieving long-term success in plastic injection moulding.


